
Peroneal Tendinopathy
Peroneal tendinopathy is a condition which occurs in response to a sudden increase in load through the foot and ankle, often repetitive activities like running and dancing.The peroneal musculature when overloaded doesn’t have the capacity to perform these activities for prolonged periods of time. As a result, the muscle tendons on the outside of your ankle can become irritated and painful.
Peroneal tendinopathy is a condition that is frequently misdiagnosed as it can present similarly to an ankle sprain. If left undiagnosed, this condition can lead to chronic ankle instability, and potentially lead to tendon rupture.
Where are your peroneals?
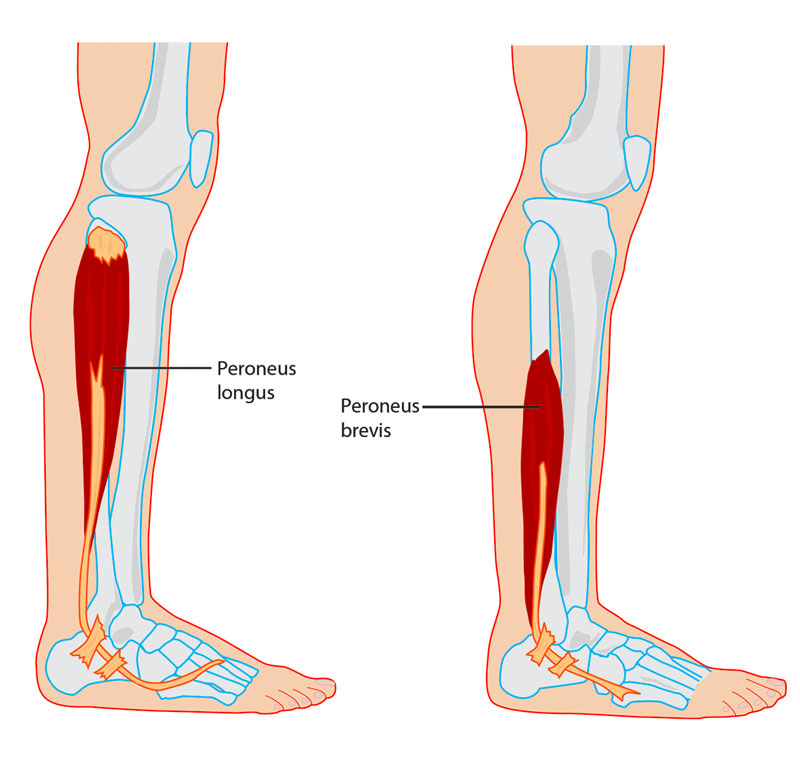
The peroneal muscles lie along the lateral (outer) aspect of the lower leg, and consist of the 3 separate muscles: peroneal longus, brevis and tertius muscles.
- The peroneal longus tendon travels to attach to the base of the first metatarsal (big toe) and medial cunineform.
- The fibularis brevis and tertius tendon attaches at the base of the fifth metatarsal (little toe)
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of peroneal tendinopathy are very similar to lateral ankle injuries.
Some of these symptoms include:
- Pain on the outside of the ankle in weight-bearing activities, such as walking, running or raising onto the toes.
- Pain on the outside of the ankle when walking on uneven surfaces.
- Pain and stiffness which is worse first thing in the morning or after a period of rest or exercise.
The cause of peroneal tendinopathy
- May develop after an acute or recurrent inversion ankle sprain
- Poor footwear
- Excessive eversion of foot
- Excessvie tightness of souls (calf muscle)
- Excessive loading of personals
How is peroneal tendinopathy treated?
Initial treatment consists of settling down the pain, with reduction of any aggravating activities and manual therapy, soft tissue, dry needling, and mobilisations. Footwear should be assessed, and orthoses may be required to address any biomechanical changes. However, the most important part of your recovery is a comprehensive progressive loaded exercise program which will be guided by your Sports Chiro or Physiotherapist.
